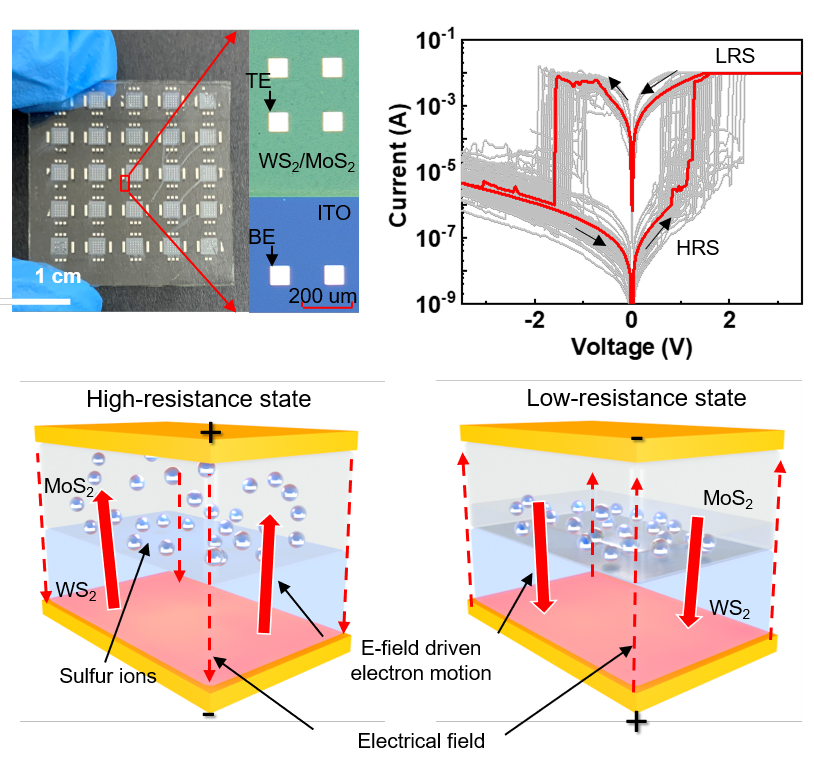
二维材料WS2/MoS2异质结忆阻器光学照片(左上图)以及多次循环电学性能测试(右上图);WS2/MoS2异质结忆阻器在外加电压作用下硫离子的运动(下图)。
忆阻器(memristor)作为一种能够模拟突触功能的两端电子元器件,被看作是突破传统冯·诺依曼计算机架构的关键器件之一。而在众多的忆阻材料体系中,基于二维材料的忆阻器器件在低功耗、高集成密度和柔性可穿戴等方面具有十分明显的优势。然而,现阶段的二维材料忆阻器架构仍以传统的三明治堆叠架构(metal-insulator-metal, MIM)为主,其器件的性能由于忆阻通道在原子层形成和熔断对材料本身可能造成不可逆的损伤而变得十分不稳定。针对该问题,熊伟教授课题组首次采用二维材料WS2/MoS2异质结结构(metal-heterojunction-metal, MHM)实现了较为稳定的忆阻器制备。与传统的MIM结构不同的是,异质结忆阻器的阻变主要是由硫离子在外加电压的作用下在异质结界面能带结构的变化导致的。最终成功实现了开关比高达104、循环次数超过120次的WS2/MoS2异质结忆阻器,相较于采用相同方法制备的单一层WS2或者MoS2忆阻器而言性能有着较大提高。这种基于MHM结构的二维材料异质结忆阻器不仅可以实现器件的高密度集成,而且可以有效提高二维材料忆阻器的稳定性,在未来数据存储和人工智能类脑计算系统上具有十分广阔的前景。
相关工作发表在Nanoscale, 2021, Advance Article. (https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR01683K)上,第一作者为张文广博士和高辉博士后,熊伟教授为通讯作者。该工作受到国家自然科学基金项目(61774067)、中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(HUST:2018KFYXKJC027)和中国博士后基金(2017M622417)等的支持。
News: A novel memristor structure-- Ultrathin memristor based on two-dimensional WS2/MoS2 heterojunction

Optical photo of 2D material WS2/MoS2 heterojunction memristor (top left) and multiple cycle electrical performance test (top right); The movement of sulfur ions in WS2/MoS2 heterojunction memristor under applied voltage (figure below).
Memristor is regarded as one of the key devices to break through the traditional Von Neumann computer architecture due to its capability of simulating the function of neural synapses. And among various memristive materials, two-dimensional (2D) material is a promising candidate to build advanced memristors with extremely high integration density and low power consumption. However, memristors based on conventional 2D material usually suffer from poor endurance and retention due to their vulnerability to material degradation during the formation/fusing processes of conductive filament channels within the switching media of 2D materials. To solve this problem, the research group of Professor Wei Xiong firstly used the 2D material WS2/MoS2 heterojunction structure (Metal-heterojunction-metal, MHM) to realize the preparation of a relatively stable memristor. Different from the conventional structure, the resistance variation of the heterojunction memristor is mainly caused by the band modulation by sulfur ions at the interface of the heterojunction under the action of applied voltage. A prototype MHM memristor based on WS2/MoS2 heterojunction is successfully developed with a large memristor switching window up to 104 and a clearly extended endurance over 120 switching cycles, showing the advantage of WS2/MoS2 heterojunction over the individual MoS2 or WS2 layers in memristive performance. It is expected that the 2D material heterojunction memristor based on the MHM structure can not only achieve high-density integration of devices but also can effectively improve the stability of 2D material memristors, which is promising for the future artificial intelligence and brain-like computing systems.
Relevant work was published in Nanoscale, 2021, Advance Article (https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR01683K), The first author is Dr. Wenguang Zhang and Postdoctoral Dr. Hui Gao, and Professor Wei Xiong is the corresponding author. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61774067), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HUST:2018KFYXKJC027) and the China Postdoctoral Foundation (2017M622417).